library(tidyverse)
library(patchwork)
load("C:/BLOG/Workspaces/NIR Soil Tutorial/post2.RData")
artifact_1000nm <- ggplot(vnir_long,
aes(x = wavelength, y = absorbance, group = sample)) +
geom_line(alpha = 0.5) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(
title = "Artifacts at 1000 nm",
subtitle = "Due to detector change",
x = 'Wavelength (nm)',
y = 'Calculated absorbance'
) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(990, 1010), ylim = c(0.4, 0.45)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 1000, linetype = "dashed", color = "red")
artifact_1830nm <- ggplot(vnir_long,
aes(x = wavelength, y = absorbance, group = sample)) +
geom_line(alpha = 0.5) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(
title = "Artifacts at 1830 nm",
subtitle = "Less visible than at 1000 nm",
x = 'Wavelength (nm)',
y = 'Calculated absorbance'
) +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(1820, 1840), ylim = c(0.2, 0.4)) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 1830, linetype = "dashed", color = "red")In this post we are going to look to the NIR spectra in detail looking for artifacts in the sample::
Plotting the spectra :
Looking to the NIR spectra we can see that there are some artifacts in the spectra at 1000 nm and 1830 nm. These artifacts are due to the change of detector in the spectrometer. We can plot these artifacts using the ggplot2 package.
In this case we are going to vave the plots and use the patchwork package to combine them.
Combining the plots
We can combine both plots:
artifact_1000nm + artifact_1830nm + plot_layout(ncol = 2)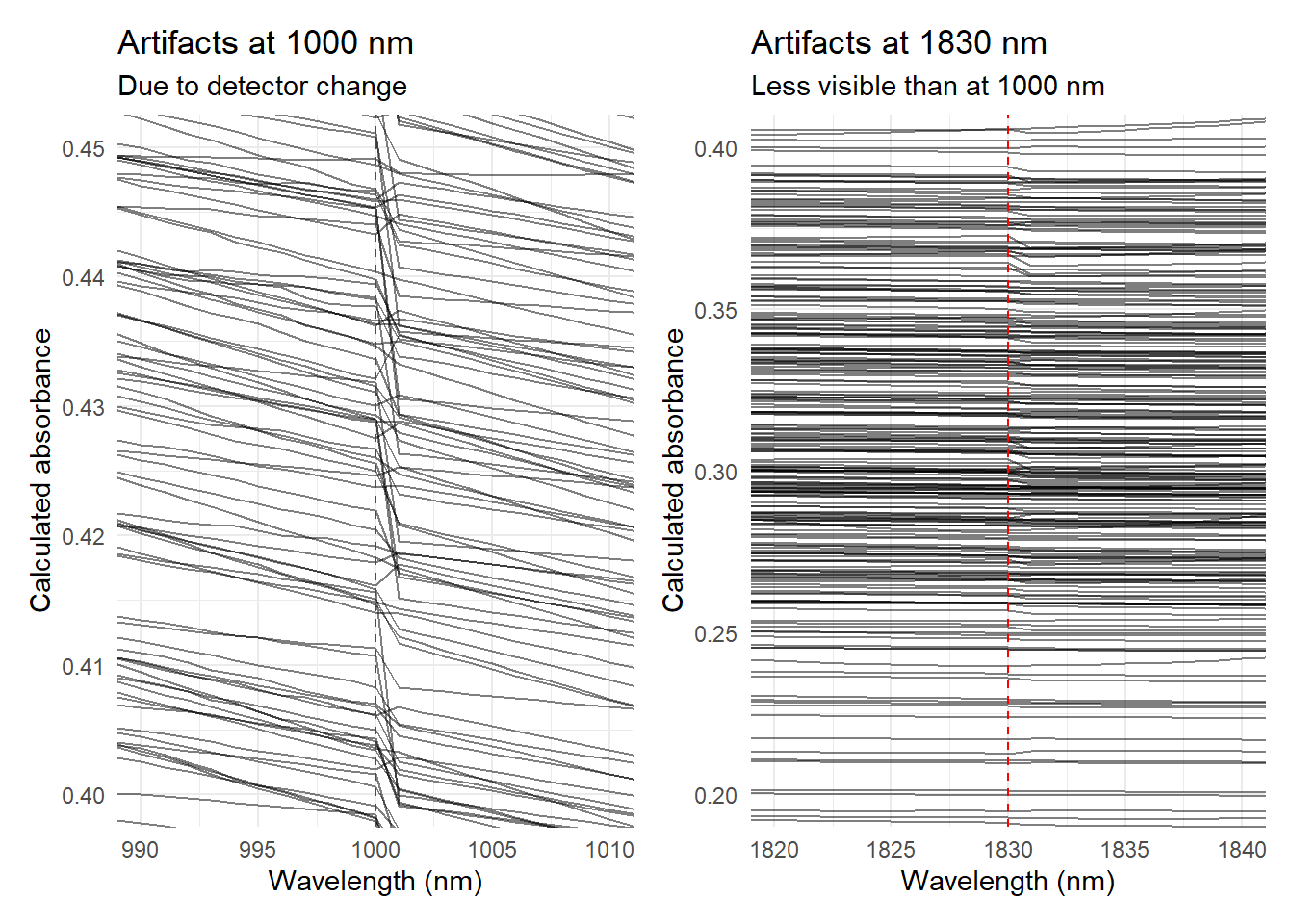
Bibliography:
Soil spectroscopy training material Wadoux, A., Ramirez-Lopez, L., Ge, Y., Barra, I. & Peng, Y. 2025. A course on applied data analytics for soil analysis with infrared spectroscopy – Soil spectroscopy training manual 2. Rome, FAO.